- All Services
- Company Co-Formating
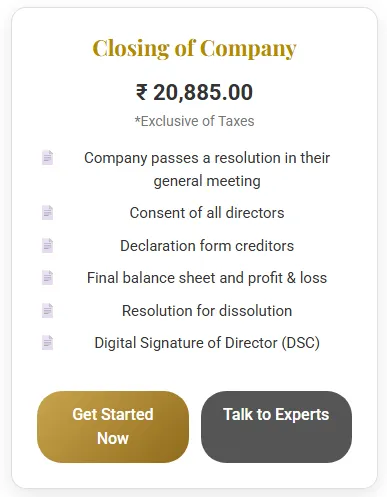
- Closing of Company
- Company Co-Formating

Closing of Company in India
Complete Legal Process, Methods & Compliance Guide
As per Companies Act, 2013 | Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
Closing of a company in India is a legally regulated process governed by the Companies Act, 2013 and administered by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Companies that are inactive, financially unviable, or no longer required must be closed legally to avoid penalties, director disqualification, and future legal action.
What Does Closing of a Company Mean?
Closing a company refers to the legal dissolution or removal of the company’s name from the Register of Companies (ROC).
- The company ceases to exist legally
- Directors are relieved from future ROC compliance
- No annual filings are required after closure
Methods of Closing a Company in India
| Method | Applicable To | Governing Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Strike Off | Inactive Companies | Section 248 – Companies Act, 2013 |
| Voluntary Liquidation | Solvent Companies | IBC, 2016 |
| Compulsory Winding Up | Defaulters / Fraud | Section 271 – Companies Act, 2013 |
Strike Off of Company (Fast Track Exit)
Eligibility Criteria
- No business operations for last 2 financial years
- No pending litigation
- No outstanding loans or liabilities
- All ROC filings completed
Applicable Companies
- Private Limited Company
- One Person Company (OPC)
- Public Company (limited cases)
Documents Required
- Board Resolution
- Special Resolution (75% shareholders)
- Director Affidavit & Indemnity Bond
- CA-certified Statement of Accounts
- PAN of Company
- Latest ITR (if filed)
Procedure
- Pass Board Resolution
- Obtain shareholder approval
- File Form STK-2 with ROC
- ROC issues public notice
- Company name removed after verification
Voluntary Liquidation of Company
Voluntary liquidation is chosen when the company is solvent but wants to shut down permanently.
Applicable Law
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016
- Voluntary Liquidation Regulations, 2017
Key Steps
- Declaration of Solvency by Directors
- Special Resolution by Shareholders
- Appointment of Liquidator
- Public Announcement
- Settlement of debts
- Final accounts & application to NCLT
- Dissolution Order
Compulsory Winding Up by Tribunal
This method applies in serious legal default cases.
- Fraud or misconduct
- Continuous default in ROC filings
- Inability to pay debts
- Company acting against national interest
Authority: National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
Post-Closure Compliance
- Directors are discharged from future compliance
- DIN remains active
- PAN becomes inactive
- No annual ROC filing required
Consequences of Not Closing Properly
- Penalties from ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh
- Director disqualification (Section 164)
- Prosecution under Companies Act
- Freezing of DIN & PAN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the easiest way to close a company? – Strike Off.
- Can a company with GST be closed? – Yes, after GST cancellation.
- Can a company with loans be closed? – No, liabilities must be cleared.
- Is CA certification mandatory? – Yes.
- Can ROC reject strike off? – Yes, if documents are incomplete.
- Is company closure reversible? – Limited restoration possible via NCLT.
Closing of Company in India
Complete Legal Process, Methods & Compliance Guide
As per Companies Act, 2013 | Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA)
Closing of a company in India is a legally regulated process governed by the Companies Act, 2013 and administered by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Companies that are inactive, financially unviable, or no longer required must be closed legally to avoid penalties, director disqualification, and future legal action.
What Does Closing of a Company Mean?
Closing a company refers to the legal dissolution or removal of the company’s name from the Register of Companies (ROC).
- The company ceases to exist legally
- Directors are relieved from future ROC compliance
- No annual filings are required after closure
Methods of Closing a Company in India
| Method | Applicable To | Governing Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Strike Off | Inactive Companies | Section 248 – Companies Act, 2013 |
| Voluntary Liquidation | Solvent Companies | IBC, 2016 |
| Compulsory Winding Up | Defaulters / Fraud | Section 271 – Companies Act, 2013 |
Strike Off of Company (Fast Track Exit)
Eligibility Criteria
- No business operations for last 2 financial years
- No pending litigation
- No outstanding loans or liabilities
- All ROC filings completed
Applicable Companies
- Private Limited Company
- One Person Company (OPC)
- Public Company (limited cases)
Documents Required
- Board Resolution
- Special Resolution (75% shareholders)
- Director Affidavit & Indemnity Bond
- CA-certified Statement of Accounts
- PAN of Company
- Latest ITR (if filed)
Procedure
- Pass Board Resolution
- Obtain shareholder approval
- File Form STK-2 with ROC
- ROC issues public notice
- Company name removed after verification
Voluntary Liquidation of Company
Voluntary liquidation is chosen when the company is solvent but wants to shut down permanently.
Applicable Law
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016
- Voluntary Liquidation Regulations, 2017
Key Steps
- Declaration of Solvency by Directors
- Special Resolution by Shareholders
- Appointment of Liquidator
- Public Announcement
- Settlement of debts
- Final accounts & application to NCLT
- Dissolution Order
Compulsory Winding Up by Tribunal
This method applies in serious legal default cases.
- Fraud or misconduct
- Continuous default in ROC filings
- Inability to pay debts
- Company acting against national interest
Authority: National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
Post-Closure Compliance
- Directors are discharged from future compliance
- DIN remains active
- PAN becomes inactive
- No annual ROC filing required
Consequences of Not Closing Properly
- Penalties from ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh
- Director disqualification (Section 164)
- Prosecution under Companies Act
- Freezing of DIN & PAN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the easiest way to close a company? – Strike Off.
- Can a company with GST be closed? – Yes, after GST cancellation.
- Can a company with loans be closed? – No, liabilities must be cleared.
- Is CA certification mandatory? – Yes.
- Can ROC reject strike off? – Yes, if documents are incomplete.
- Is company closure reversible? – Limited restoration possible via NCLT.
Alternative Products
These other products might interest you